
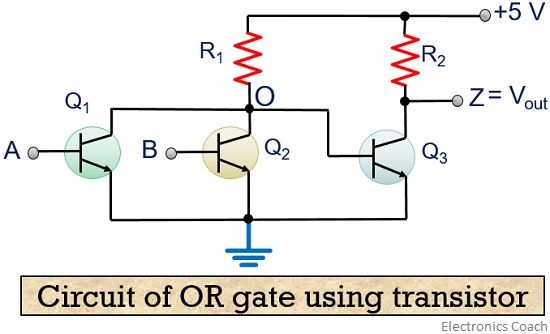
Bias is removed from Q3’s base when Q1 switches on. This then delivers bias to Q3 which turns it on and locks the output to ground. With Q1 switched off, its collector becomes close to the supply voltage.
#ONE TRANSISTOR GATE CIRCUITS DRIVER#
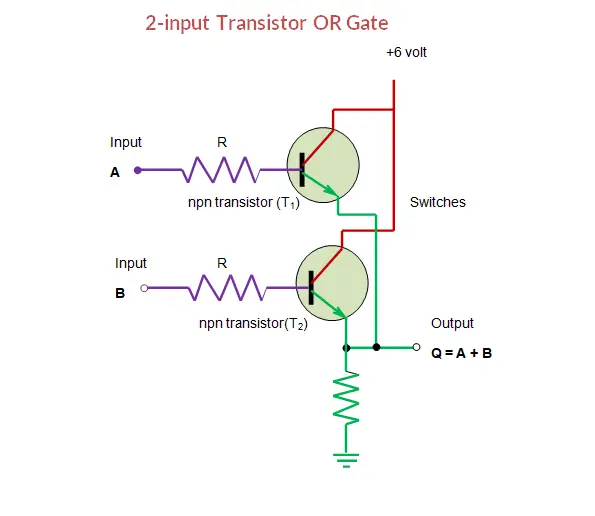
Furthermore, if the circuit has a driver whose connection needs the load to be arrested to ground, transistor Q3 must be added. Up until this point, our analysis of transistor logic circuits has been limited to the TTL design paradigm, whereby bipolar transistors are used, and the general strategy of floating inputs being equivalent to high (connected to V cc) inputsand correspondingly, the allowance of open-collector output stagesis maintained. Once Q2 is off, it will not sink any current from its output. When the input is low, Q1 and Q2 are switched off. This means that the circuit’s output is the supply voltage sans the voltage drop identified across Q2 and R4. Simultaneously, the low at Q1’s collector is also applied to the base of Q3 which causes it to switch off. Once a positive input is applied to Q1’s base, it switches the transistor on, pulling the base of Q2 low and turning Q2 on. Hence, we will describe the circuit a little. You can also use earphones having an impedance of around 500 ohms instead of the recommended speaker. The loudspeaker is a tiny piece having a coil impedance of about 25 to 40 ohms. Not quite same like the last circuit, this one is a little complicated. This simple beeper circuit is built around an assymetric multivibrator initialized through a pushbutton. The truth table shows that a high input delivers a high output, whereas a low input provides a low output. The circuit in the following figure shows a BJT equivalent of logic non-inverting amplifier and buffer stage that can be utilised to elevate output drive current. The magnitude of current the transistor can sink relies on its gain and power modulating capabilities.
Once the inverter’s output goes low, the attached circuit network which is connected to its output will be arrested to ground. When the output of the BJT inverter is high, it will channel the drive current which is restricted only by the value of R2 and the transistor to whatever circuit network that is attached to its output. Size comparison of bipolar junction transistor packages, including (from left to right): SOT-23, TO-92, TO-126, and TO-3. In short, high in, low out low in, high out. The truth table for this circuit is quite similar as what one would expect from a common integrated-circuit logic inverter. 7 How many transistors are there in a logic gate If anybody asks me, I tell them: A NOT gate is 1 transistor. This function is generally similar to the standard OR function with one. The circuit as depicted in Figure below is a standard inverting amplifier that can be powered from most CMOS of TTL ICs. An electronic XOR (Exclusive OR) gate performs the digital logic XOR function.
#ONE TRANSISTOR GATE CIRCUITS HOW TO#
In the following circuits we learn how to make simple logic equivalent inverter and buffer amplifier stages using discrete BJTs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
